概念
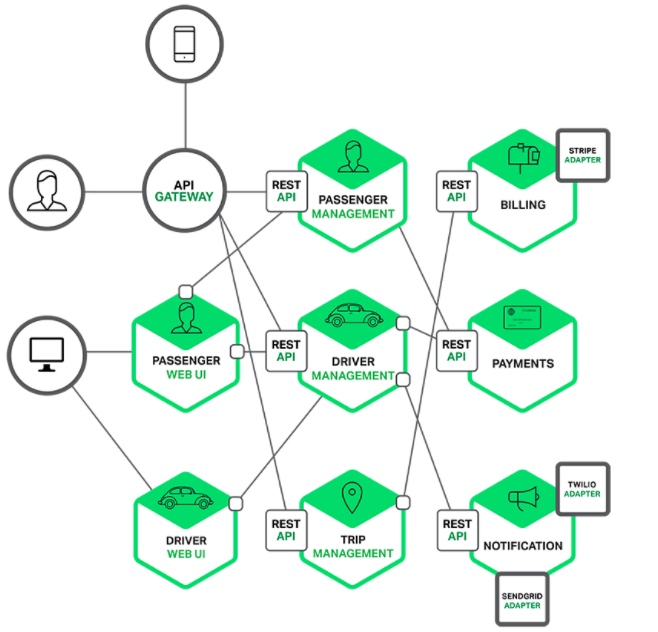
当我们把系统微服务化后,想查询某个接口一次请求的耗时信息,需要登录多台机器查询相关日志才行。 如下图所示架构,当对应服务集群化部署后,想要查询到某一次请求信息更是难上加难。那我们有什么办法可以解决这个问题么?
答案当然是有的,分布式追踪系统正是为了解决这个问题而生。分布式跟踪为描述和分析跨进程事务提供了一种解决方案。如Google Dapper论文 (业界的分布式追踪系统基本都是以这篇论文为基础进行实现)所述,分布式跟踪的一些使用场景包括:
- 异常检测,问题诊断
- 分布式系统内各组件的调用情况
- 性能/延迟优化
- 服务依赖性分析
因为业界分布式追踪系统众多,各家Api定义上有一定的差异,为了统一标准,于是OpenTracing出现了。
什么是OpenTracing?
OpenTracing通过提供平台无关、厂商无关的API,使得开发人员能够方便的添加或更换追踪系统的实现。OpenTracing正在为全球的分布式追踪,提供统一的概念和数据标准。
除了OpenTracing外,还有OpenCensus 这个项目,OpenCensus 由google发起,它除了包含tracing外,还包含度量(metrics)。
两套分布式追踪框架,都有很多追随者,都想统一对方,但最终结果是对峙不下,最后两个组织一起组队新建了OpenTelemetry项目。项目的第一宗旨就是:兼容OpenTracing和OpenSensus。对于使用OpenTracing或OpenSensus的应用不需要重新改动就可以接入OpenTelemetry。
模型
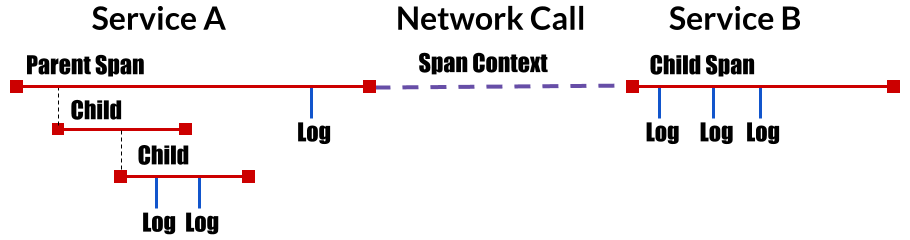
从应用角度看分布式追踪系统所处的位置
示例
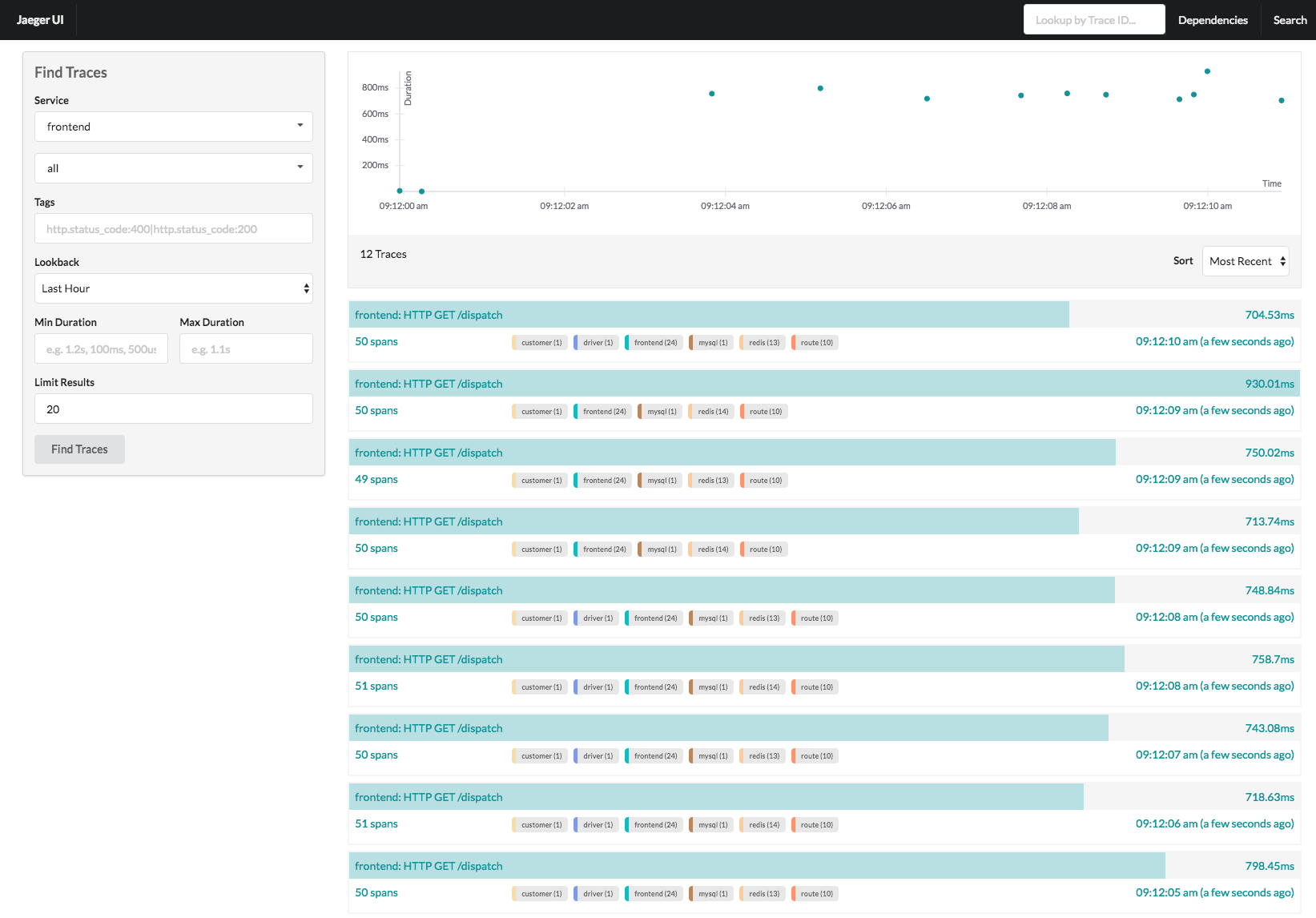
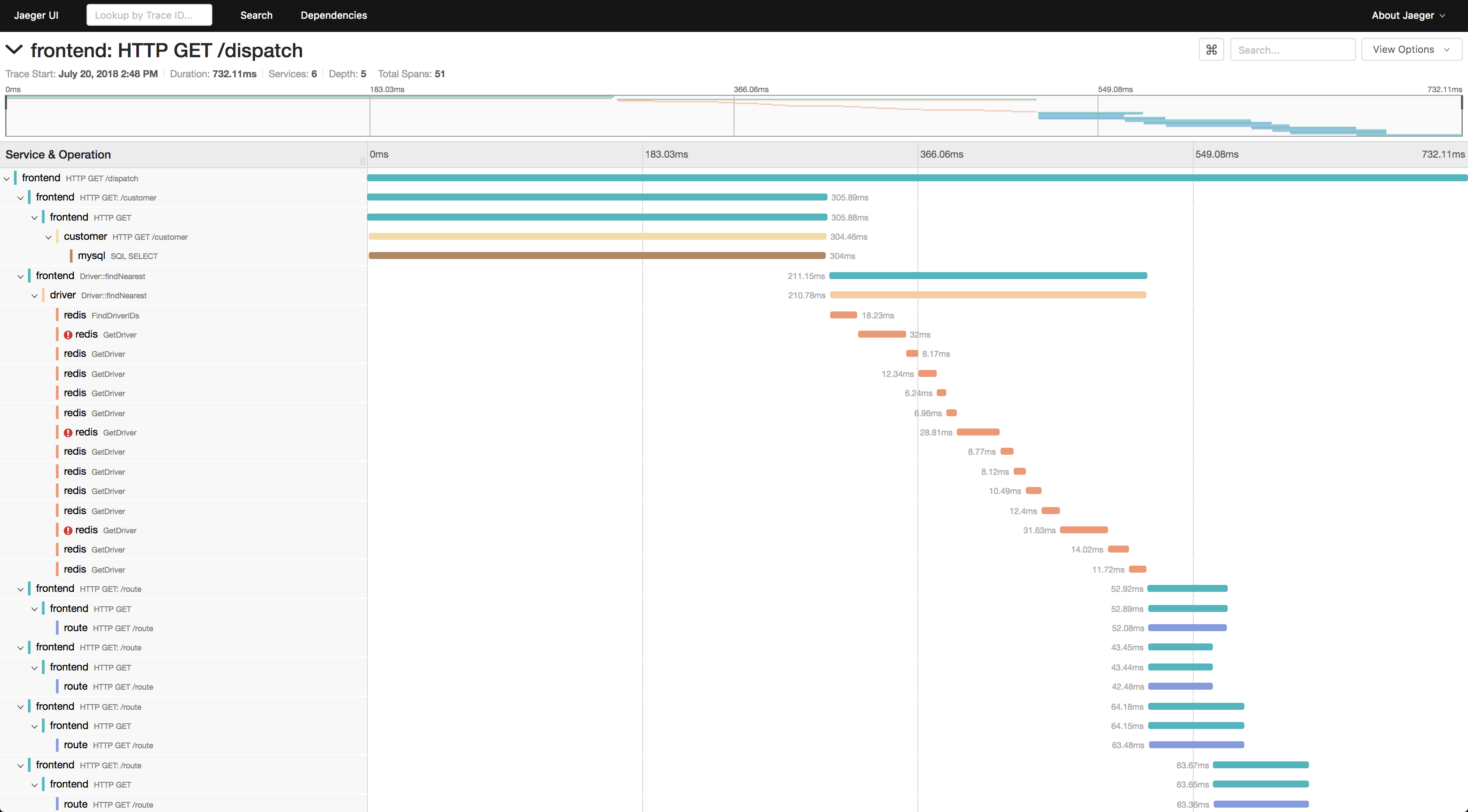
先来看两张效果图感受一下(以jaeger ui为例)
语义
这里的语义以 OpenTracing 为基础。
数据模型
1 | [Span A] ←←←(the root span) |
时序图
有些时候,使用下面这种基于时间轴的时序图可以更好的展现Trace(调用链)
1 | ––|–––––––|–––––––|–––––––|–––––––|–––––––|–––––––|–––––––|–> time |
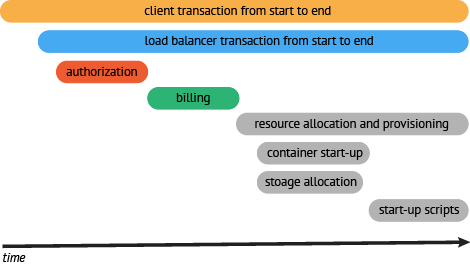
这种展现方式增加显示了执行时间的上下文,相关服务间的层次关系,进程或者任务的串行或并行调用关系。这样的视图有助于发现系统调用的关键路径。通过关注关键路径的执行过程,项目团队可专注于优化路径中的关键位置,最大幅度的提升系统性能。
Trace
一条Trace是指一个请求包含的调用链(包含下游所有请求的调用链), 一条Trace可以被认为是一个由多个Span组成的有向无环图, Span与Span的关系被命名为References。
Operation Names
每一个Span都有一个操作名称,这个名称简单,并具有可读性高。(例如:一个RPC方法的名称,一个函数名,或者一个大型计算过程中的子任务或阶段)
Span
一个Span代表系统中具有开始时间和执行时长的逻辑运行单元 。具体可以理解为一次方法调用, 一个程序块的调用或者一次RPC/数据库访问。
每个Span包含以下的状态:
- An operation name,操作名称
- A start timestamp,起始时间
- A finish timestamp,结束时间
- Span Tags,一组键值对构成的Span标签集合。键值对中,键必须为string,值可以是字符串,布尔,或者数字类型。
- Span Logs,一组span的日志集合。 每次log操作包含一个键值对,以及一个时间戳。 键值对中,键必须为string,值可以是任意类型。 但是需要注意,不是所有的支持OpenTracing的Tracer,都需要支持所有的值类型。
- SpanContext,Span上下文对象 (下面会详细说明)
- References(Span间关系),相关的零个或者多个Span(Span间通过SpanContext建立这种关系)
每一个SpanContext包含以下状态:
- 任何一个OpenTracing的实现,都需要将当前调用链的状态(例如: spanID 和traceID ),依赖一个独特的Span去跨进程边界传输
- Baggage Items,Trace的随行数据,是一个键值对集合,它存在于trace中,也需要跨进程边界传输
References
一个Span可以和一个或者多个Span间存在因果关系。 OpenTracing定义了两种关系:ChildOf 和 FollowsFrom。这两种引用类型代表了子节点和父节点间的直接因果关系。
ChildOf 引用
一个Span可能是一个父级Span的孩子,即ChildOf 关系。在ChildOf 引用关系下,父级span某种程度上取决于子Span。下面这些情况会构成ChildOf 关系:
一个RPC调用的服务端的Span,和RPC服务客户端的Span构成
ChildOf关系一个sql insert操作的Span,和ORM的save方法的Span构成
ChildOf关系很多span可以并行工作(或者分布式工作)都可能是一个父级的Span的子项,他会合并所有子Span的执行结果,并在指定期限内返回
下面表述一个
ChildOf关系的父子节点关系的时序图:
FollowsFrom 引用
一些父级节点不以任何方式依然他们子节点的执行结果,这种情况下,我们说这些子Span和父Span之间是FollowsFrom 的因果关系。
下面表述一个FollowsFrom 关系的父子节点关系的时序图:
1 | [-Parent Span-] [-Child Span-] |
Tags
每个Span可以有多个键值对(key:value)形式的Tags,Tags是没有时间戳的,支持简单的对Span进行注解和补充。 Span的tag不会跨进程传输,因此它们不会被子级的span继承。
必填参数
tag key,必须是string类型
tag value,类型为字符串,布尔或者数字
注意,OpenTracing标准包含“standard tags,标准Tag”,此文档中定义了Tag的标准含义。
| Tag名称 | 字段类型 | 字段解释及示例 |
|---|---|---|
component |
string | The software package, framework, library, or module that generated the associated Span. E.g., "grpc", "django", "JDBI". |
db.instance |
string | Database instance name. E.g., In java, if the jdbc.url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/customers", the instance name is "customers". |
db.statement |
string | A database statement for the given database type. E.g., for db.type="sql", "SELECT * FROM wuser_table"; for db.type="redis", "SET mykey 'WuValue'". |
db.type |
string | Database type. For any SQL database, "sql". For others, the lower-case database category, e.g. "cassandra", "hbase", or "redis". |
db.user |
string | Username for accessing database. E.g., "readonly_user" or "reporting_user" |
error |
bool | true if and only if the application considers the operation represented by the Span to have failed |
http.method |
string | HTTP method of the request for the associated Span. E.g., "GET", "POST" |
http.status_code |
integer | HTTP response status code for the associated Span. E.g., 200, 503, 404 |
http.url |
string | URL of the request being handled in this segment of the trace, in standard URI format. E.g., "https://domain.net/path/to?resource=here" |
message_bus.destination |
string | An address at which messages can be exchanged. E.g. A Kafka record has an associated "topic name" that can be extracted by the instrumented producer or consumer and stored using this tag. |
peer.address |
string | Remote “address”, suitable for use in a networking client library. This may be a "ip:port", a bare "hostname", a FQDN, or even a JDBC substring like "mysql://prod-db:3306" |
peer.hostname |
string | Remote hostname. E.g., "opentracing.io", "internal.dns.name" |
peer.ipv4 |
string | Remote IPv4 address as a .-separated tuple. E.g., "127.0.0.1" |
peer.ipv6 |
string | Remote IPv6 address as a string of colon-separated 4-char hex tuples. E.g., "2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334" |
peer.port |
integer | Remote port. E.g., 80 |
peer.service |
string | Remote service name (for some unspecified definition of "service"). E.g., "elasticsearch", "a_custom_microservice", "memcache" |
sampling.priority |
integer | If greater than 0, a hint to the Tracer to do its best to capture the trace. If 0, a hint to the trace to not-capture the trace. If absent, the Tracer should use its default sampling mechanism. |
span.kind |
string | Either "client" or "server" for the appropriate roles in an RPC, and "producer" or "consumer" for the appropriate roles in a messaging scenario. |
Logs
每个Span可以进行多次Logs操作,每一次Logs操作,都需要一个带时间戳的时间名称,以及可选的任意大小的存储结构。
必填参数
- 一个或者多个键值对,其中键必须是字符串类型,值可以是任意类型。某些OpenTracing实现,可能支持更多的log值类型。
可选参数
一个明确的时间戳。如果指定时间戳,那么它必须在span的开始和结束时间之内。
注意,OpenTracing标准包含“standard log keys,标准log的键”,此文档中定义了这些键的标准含义。
| Log名称 | 字段类型 | 字段解释及示例 |
|---|---|---|
error.kind |
string | The type or “kind” of an error (only for event="error" logs). E.g., "Exception", "OSError" |
error.object |
object | For languages that support such a thing (e.g., Java, Python), the actual Throwable/Exception/Error object instance itself. E.g., A java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException instance, a python exceptions.NameError instance |
event |
string | A stable identifier for some notable moment in the lifetime of a Span. For instance, a mutex lock acquisition or release or the sorts of lifetime events in a browser page load described in the Performance.timing specification. E.g., from Zipkin, "cs", "sr", "ss", or "cr". Or, more generally, "initialized" or "timed out". For errors, "error" |
message |
string | A concise, human-readable, one-line message explaining the event. E.g., "Could not connect to backend", "Cache invalidation succeeded" |
stack |
string | A stack trace in platform-conventional format; may or may not pertain to an error. E.g., "File \"example.py\", line 7, in \\ncaller()\nFile \"example.py\", line 5, in caller\ncallee()\nFile \"example.py\", line 2, in callee\nraise Exception(\"Yikes\")\n" |
SpanContext
SpanContext更多的是一个“概念” 。每个Span都必须提供方法访问SpanContext。SpanContext代表跨越进程边界,传递到下级Span的状态,并用于封装Baggage 。 OpenTracing的使用者仅仅需要,在创建Span、向传输协议Inject(注入)和从传输协议中Extract(提取)时使用 。
Baggage
Baggage元素是一个键值对集合,将这些值设置给给定的Span,Span的SpanContext,以及所有和此Span有直接或者间接关系的本地Span。 也就是说,baggage元素随Trace一起应用程序调用过程 一同传播
Baggage拥有强大功能,也会有很大的消耗。由于Baggage的全局传输,如果包含的数量量太大,或者元素太多,它将降低系统的吞吐量或增加RPC的延迟。
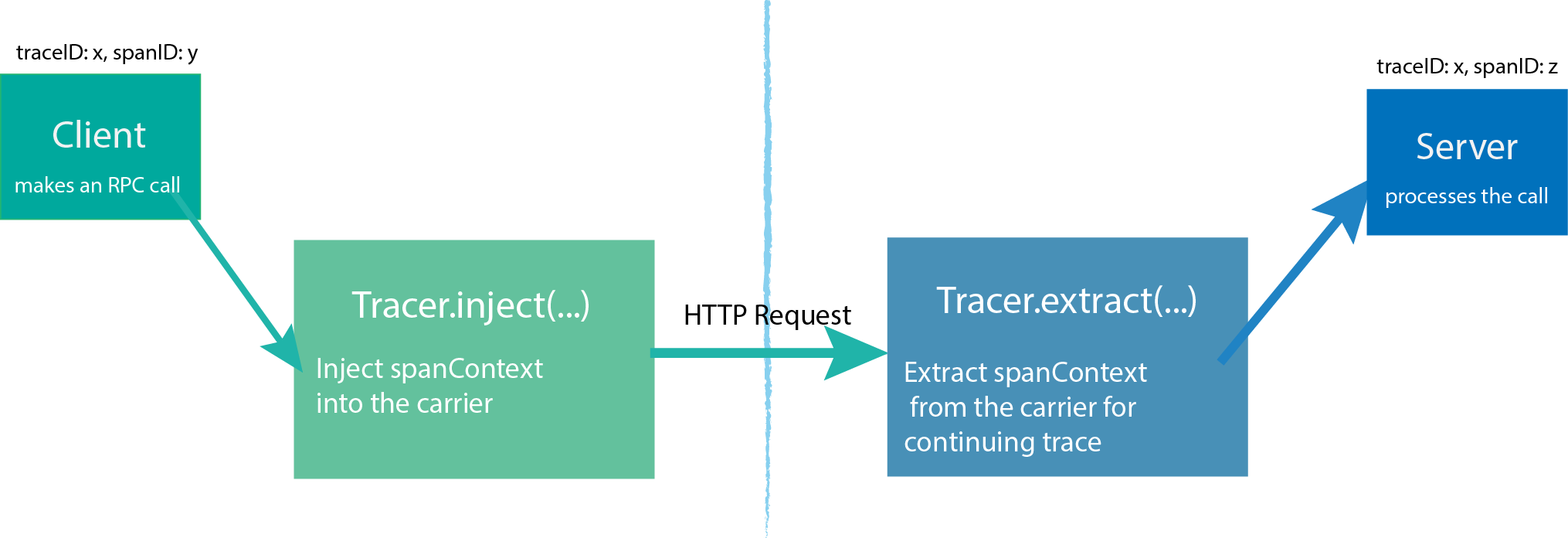
Inject and Extract
SpanContext可以通过Injected操作向Carrier增加,或者通过Extracted从Carrier中获取,跨进程通讯数据。通过这种方式,SpanContexts可以跨越进程边界,并提供足够的信息来建立跨进程的span间关系(因此可以实现跨进程连续追踪)。
Inject 类比传递序列化后的参数
Extract 反序列化Inject的参数值
传递方式例如:
- 依赖HTTP头传递(B3-header)
- Dubbo 定制Filter通过 RpcContext 设置 Attachment 来传递
Carrier可以是一个接口或者一个数据载体,他对于跨进程通讯是十分有帮助的。Carrier负责将追踪状态从一个进程”carries”传递到另一个进程 。OpenTracing规定所有平台的实现者支持两种Carrier格式:基于”text map”(基于字符串的map)的格式和基于”binary”(二进制)的格式。
- text map 格式的 Carrier是一个平台惯用的map格式,基于unicode编码的
字符串对字符串键值对 - binary 格式的 Carrier 是一个不透明的二进制数组(更紧凑和有效)
开源
语言支持
框架支持
- CNCF Jaeger
- LightStep
- Instana
- Apache SkyWalking
- inspectIT
- stagemonitor
- Datadog
- Wavefront by VMware
- Elastic APM
通过cncf社区链接也可以查询到相关框架
https://landscape.cncf.io/category=tracing&format=card-mode&grouping=category

框架选型
如果公司用的Java体系可以选择 Zipkin 或者 SkyWalking 。Zipkin 主要是tracing,而SkyWalking整体是APM,包含tracing。如果不打算做二次开发建议选SkyWalking,开箱即用(目前存储主要支持ElasticSearch)。
目前云原生体系在大力推Jaeger (Go语言研发),如果公司有go体系,也是个不错的选择。
参考文献
https://github.com/opentracing/specification
https://github.com/opentracing-contrib